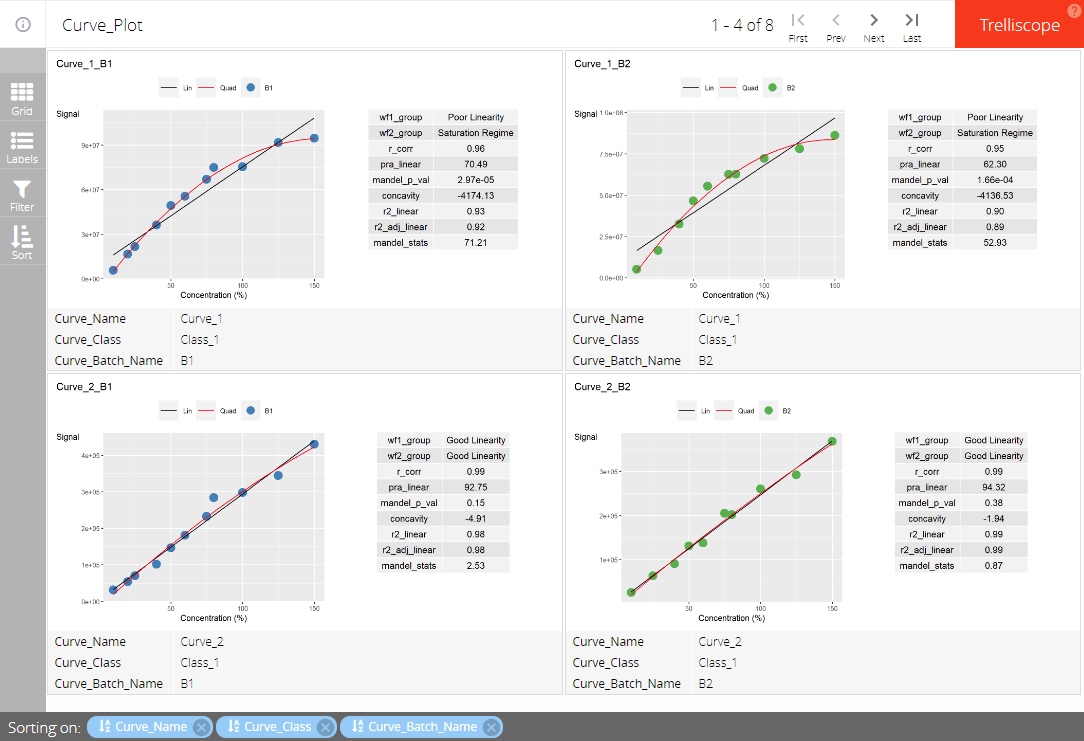
Here is an example to output plot in ggplot2 into
trellis. The example in plotly can be found in vignette
“Plots in plotly”.
library(lancer)
# Data Creation
concentration <- c(
10, 20, 25, 40, 50, 60,
75, 80, 100, 125, 150,
10, 25, 40, 50, 60,
75, 80, 100, 125, 150
)
curve_batch_name <- c(
"B1", "B1", "B1", "B1", "B1",
"B1", "B1", "B1", "B1", "B1", "B1",
"B2", "B2", "B2", "B2", "B2",
"B2", "B2", "B2", "B2", "B2"
)
sample_name <- c(
"Sample_010a", "Sample_020a",
"Sample_025a", "Sample_040a", "Sample_050a",
"Sample_060a", "Sample_075a", "Sample_080a",
"Sample_100a", "Sample_125a", "Sample_150a",
"Sample_010b", "Sample_025b",
"Sample_040b", "Sample_050b", "Sample_060b",
"Sample_075b", "Sample_080b", "Sample_100b",
"Sample_125b", "Sample_150b"
)
curve_1_saturation_regime <- c(
5748124, 16616414, 21702718, 36191617,
49324541, 55618266, 66947588, 74964771,
75438063, 91770737, 94692060,
5192648, 16594991, 32507833, 46499896,
55388856, 62505210, 62778078, 72158161,
78044338, 86158414
)
curve_2_good_linearity <- c(
31538, 53709, 69990, 101977, 146436, 180960,
232881, 283780, 298289, 344519, 430432,
25463, 63387, 90624, 131274, 138069,
205353, 202407, 260205, 292257, 367924
)
curve_3_noise_regime <- c(
544, 397, 829, 1437, 1808, 2231,
3343, 2915, 5268, 8031, 11045,
500, 903, 1267, 2031, 2100,
3563, 4500, 5300, 8500, 10430
)
curve_4_poor_linearity <- c(
380519, 485372, 478770, 474467, 531640, 576301,
501068, 550201, 515110, 499543, 474745,
197417, 322846, 478398, 423174, 418577,
426089, 413292, 450190, 415309, 457618
)
curve_batch_annot <- tibble::tibble(
Sample_Name = sample_name,
Curve_Batch_Name = curve_batch_name,
Concentration = concentration
)
curve_data <- tibble::tibble(
Sample_Name = sample_name,
`Curve_1` = curve_1_saturation_regime,
`Curve_2` = curve_2_good_linearity,
`Curve_3` = curve_3_noise_regime,
`Curve_4` = curve_4_poor_linearity
)
curve_table <- lancer::create_curve_table(
curve_batch_annot = curve_batch_annot,
curve_data_wide = curve_data,
common_column = "Sample_Name",
signal_var = "Signal",
column_group = "Curve_Name"
)
curve_classified <- curve_table |>
lancer::summarise_curve_table(
grouping_variable = c(
"Curve_Name",
"Curve_Batch_Name"
),
conc_var = "Concentration",
signal_var = "Signal"
) |>
dplyr::arrange(.data[["Curve_Name"]]) |>
lancer::evaluate_linearity(
grouping_variable = c(
"Curve_Name",
"Curve_Batch_Name"
))Here is the output of curve_table and
curve_classified
print(head(curve_table), width = 100)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> Sample_Name Curve_Batch_Name Concentration Curve_Name Signal
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 Sample_010a B1 10 Curve_1 5748124
#> 2 Sample_010a B1 10 Curve_2 31538
#> 3 Sample_010a B1 10 Curve_3 544
#> 4 Sample_010a B1 10 Curve_4 380519
#> 5 Sample_020a B1 20 Curve_1 16616414
#> 6 Sample_020a B1 20 Curve_2 53709
print(head(curve_classified), width = 100)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 11
#> Curve_Name Curve_Batch_Name wf1_group wf2_group r_corr pra_linear
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Curve_1 B1 Poor Linearity Saturation Regime 0.963 70.5
#> 2 Curve_1 B2 Poor Linearity Saturation Regime 0.950 62.3
#> 3 Curve_2 B1 Good Linearity Good Linearity 0.990 92.8
#> 4 Curve_2 B2 Good Linearity Good Linearity 0.995 94.3
#> 5 Curve_3 B1 Poor Linearity Noise Regime 0.964 71.2
#> 6 Curve_3 B2 Poor Linearity Noise Regime 0.978 74.7
#> mandel_p_val concavity r2_linear r2_adj_linear mandel_stats
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0.0000297 -4174. 0.928 0.920 71.2
#> 2 0.000166 -4137. 0.903 0.890 52.9
#> 3 0.150 -4.91 0.980 0.978 2.53
#> 4 0.382 -1.94 0.990 0.988 0.868
#> 5 0.00000678 0.468 0.930 0.922 106.
#> 6 0.00256 0.321 0.956 0.951 20.9We then create the ggplot plots with
curve_table and curve_classified
# Create a trellis table
trellis_table_orig <- lancer::add_ggplot_panel(
curve_table = curve_table,
curve_summary = curve_classified,
grouping_variable = c(
"Curve_Name",
"Curve_Batch_Name"
),
curve_batch_var = "Curve_Batch_Name",
curve_batch_col = c(
"#377eb8",
"#4daf4a"
),
conc_var = "Concentration",
conc_var_units = "%",
conc_var_interval = 50,
signal_var = "Signal",
plot_first_half_lin_reg = FALSE
)
trellis_list_orig <- trellis_table_orig$panelTo output these plots as a trellis in html, convert the
grouping_variable as conditional variable, the
column holding the plots as a panel_variable and the other
columns as common cognostics.
We use the function convert_to_cog which uses the
default cog_df created by
create_default_cog_df.
lancer::create_default_cog_df()
#> col_name_vec desc_vec type_vec
#> 1 Curve_Name Curve_Name factor
#> 2 Curve_Batch_Name Curve_Batch_Name factor
#> 3 Curve_Class Classes of Curves factor
#> 4 wf1_group Group from workflow 1 factor
#> 5 wf2_group Group from workflow 2 factor
#> 6 r_corr Pearson Correlation R values numeric
#> 7 pra_linear Linear Regression Percent Residual Accuracy numeric
#> 8 mandel_p_val P values for Mandel test numeric
#> 9 r2_linear Linear Regression R^2 Value numeric
#> 10 r2_adj_linear Linear Regression Adjusted R^2 Value numeric
#> 11 mandel_stats Test statistics for Mandel Test numeric
#> 12 adl_value Average Deviation from Linearity numericUsing the function convert_to_cog,
trellis_table_convert <- trellis_table_orig |>
lancer::convert_to_cog(
grouping_variable = c(
"Curve_Name",
"Curve_Batch_Name"
),
panel_variable = "panel"
)The output is as follows.
print(head(trellis_table_convert), width = 100)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 12
#> Curve_Name Curve_Batch_Name wf1_group wf2_group r_corr pra_linear
#> <cog> <cog> <cog> <cog> <cog> <cog>
#> 1 Curve_1 B1 Poor Linearity Saturation Reg… 0.963362 70.49412
#> 2 Curve_2 B1 Good Linearity Good Linearity 0.989903 92.75456
#> 3 Curve_3 B1 Poor Linearity Noise Regime 0.964252 71.18372
#> 4 Curve_4 B1 Poor Linearity Poor Linearity 0.311458 -251.44937
#> 5 Curve_1 B2 Poor Linearity Saturation Reg… 0.950007 62.30351
#> 6 Curve_2 B2 Good Linearity Good Linearity 0.994815 94.32046
#> mandel_p_val concavity r2_linear r2_adj_linear mandel_stats panel
#> <cog> <cog> <cog> <cog> <cog> <trllscp_>
#> 1 2.968599e-05 -4174.1333061 0.928067 0.920074 71.2051525 <patchwrk>
#> 2 1.501138e-01 -4.9071785 0.979908 0.977675 2.5335524 <patchwrk>
#> 3 6.775079e-06 0.4677827 0.929783 0.921981 106.2121740 <patchwrk>
#> 4 6.599208e-03 -20.5225862 0.097006 -0.003327 13.2417851 <patchwrk>
#> 5 1.662149e-04 -4136.5254757 0.902514 0.890328 52.9344641 <patchwrk>
#> 6 3.824145e-01 -1.9381407 0.989657 0.988364 0.8684023 <patchwrk>Observe that the attributes of the columns are different. For the grouping variable column labelled we have
print(attributes(trellis_table_convert$Curve_Name))
#> $cog_attrs
#> $cog_attrs$desc
#> [1] "conditioning variable"
#>
#> $cog_attrs$type
#> [1] "factor"
#>
#> $cog_attrs$group
#> [1] "condVar"
#>
#> $cog_attrs$defLabel
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $cog_attrs$defActive
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $cog_attrs$filterable
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $cog_attrs$log
#> [1] NA
#>
#>
#> $class
#> [1] "cog" "character"For the column labelled as a panel_variable, we have
print(attributes(trellis_table_convert$panel))
#> $class
#> [1] "trelliscope_panels" "list"For the rest of the column converted to a common cognostics, we have
print(attributes(trellis_table_convert$r_corr))
#> $cog_attrs
#> $cog_attrs$desc
#> [1] "Pearson Correlation R values"
#>
#> $cog_attrs$type
#> [1] "numeric"
#>
#> $cog_attrs$group
#> [1] "common"
#>
#> $cog_attrs$defLabel
#> [1] FALSE
#>
#> $cog_attrs$defActive
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $cog_attrs$filterable
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $cog_attrs$log
#> [1] NA
#>
#>
#> $class
#> [1] "cog" "numeric"It is also possible for users to create their own cognostics as well.
curve_name <- c("Curve_1", "Curve_2", "Curve_3", "Curve_4")
curve_class <- c("Class_1", "Class_1", "Class_2", "Class_2")
curve_name_annot <- tibble::tibble(
Curve_Name = curve_name,
Curve_Class = curve_class
)
col_name_vec <- c("Curve_Name", "Curve_Class")
desc_vec <- c(
"Names of Curves",
"Classes of Curves"
)
type_vec <- c("factor", "factor")
cog_df <- data.frame(
col_name_vec = col_name_vec,
desc_vec = desc_vec,
type_vec = type_vec
)
trellis_table_orig_converted <- trellis_table_orig |>
dplyr::left_join(curve_name_annot, by = "Curve_Name") |>
lancer::convert_to_cog(
cog_df = cog_df,
grouping_variable = c(
col_name_vec,
"Curve_Batch_Name"
),
panel_variable = "panel",
col_name_vec = "col_name_vec",
desc_vec = "desc_vec",
type_vec = "type_vec"
)The list of ggplots can be output as follows by calling
this command in the R console:
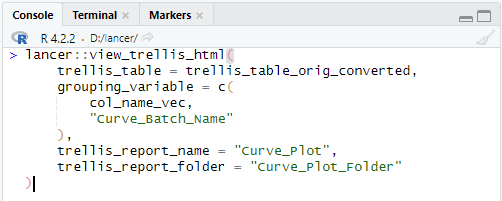
lancer::view_trellis_html(
trellis_table = trellis_table_orig_converted,
grouping_variable = c(
col_name_vec,
"Curve_Batch_Name"
),
trellis_report_name = "Curve_Plot",
trellis_report_folder = "Curve_Plot_Folder"
)
This will create a folder called “Curve_Plot_Folder” as defined by
trellis_report_folder in your current working
directory.
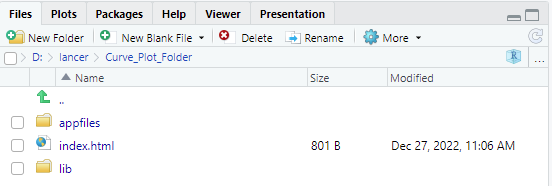
You may view the plots by clicking on “index.html”